Note
Click here to download the full example code
Comparison of mixed-norm models¶
This example compares the Group Lasso, Dirty models and multilevel Lasso.
DirtyModel estimates a set of sparse coefficients for multiple regression models that share a fraction of non-zero features. It is a generalization of The GroupLasso estimator. It also takes a 3D X (n_tasks, n_samples, n_features) and a 2D y (n_tasks, n_samples).
DirtyModel solves the optimization problem:
(1 / (2 * n_samples)) * ||Y - X(W_1 + W_2)||^2_Fro + alpha * ||W_1||_21
+ beta * ||W_2||_1
Where:
||W||_21 = \sum_i \sqrt{\sum_j w_ij^2}
i.e. the sum of norm of each row. and:
||W||_1 = \sum_i \sum_j |w_ij|
The multi-level Lasso uses instead a product decomposition. The optimization objective for the Multilevel Lasso is:
(1 / (2 * n_samples)) * ||Y - XW||^2_Fro + alpha ||W||_{1 0.5}
Where::
||W||_{1 0.5} = sum_j sqrt(||W_j||_1)
Which is equivelent to the product decomposition:
(1 / (2 * n_samples)) * ||Y - X(C[:, None] * S)||^2_Fro
+ beta * ||C||_1 + gamma * ||S||_1
Where::
C in R^n_features
S in R^(n_features, n_tasks)
alpha = 2 * sqrt(beta * gamma)
# Author: Hicham Janati (hicham.janati@inria.fr)
#
# License: BSD (3-clause)
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from mutar import DirtyModel, MultiLevelLasso, IndLasso, GroupLasso
Generate multi-task data
rng = np.random.RandomState(42)
n_tasks, n_samples, n_features = 10, 20, 50
X = rng.randn(n_tasks, n_samples, n_features)
# generate random coefficients and make it sparse
# select support
support = rng.rand(n_features, n_tasks) > 0.97
coef = support * rng.randn(n_features, n_tasks)
# make features 0, 2, 4 and 6 shared
coef[:7:2] = rng.randn(4, n_tasks)
y = np.array([x.dot(c) for x, c in zip(X, coef.T)])
# add noise
y += 0.2 * np.std(y) + rng.randn(n_tasks, n_samples)
Lasso fit
alpha = 0.5 * np.ones(n_tasks)
lasso = IndLasso(alpha=alpha)
lasso.fit(X, y)
Group Lasso fit
alpha = 1.75
gl = GroupLasso(alpha=alpha)
gl.fit(X, y)
Dirty models fit
alpha = 0.8
beta = 0.4
dirty = DirtyModel(alpha=alpha, beta=beta)
dirty.fit(X, y)
Multilevel Lasso fit
alpha = 0.25
mll = MultiLevelLasso(alpha=alpha)
mll.fit(X, y)
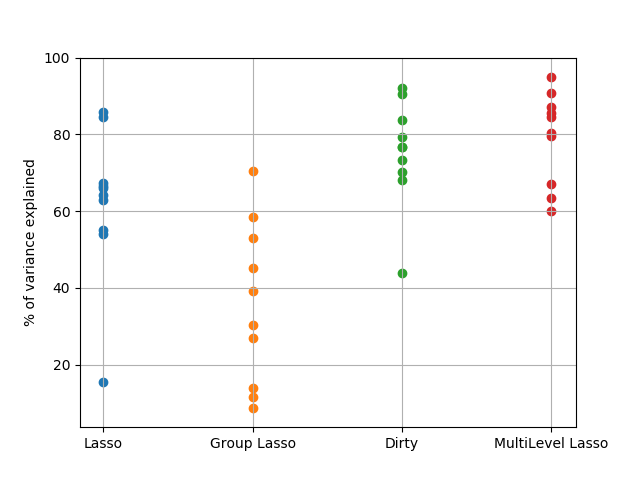
we show the R2 scores for each model. Each dot corresponds to a task.
models = [None, lasso, gl, dirty, mll]
names = ["Truth", "Lasso", "Group Lasso", "Dirty", "MultiLevel Lasso"]
f, ax = plt.subplots(1, 1)
for i, (name, model) in enumerate(zip(names[1:], models[1:])):
r2 = model.score(X, y)
ax.scatter(n_tasks * [i + 1], 100 * r2)
ax.set_ylabel("% of variance explained")
ax.set_xticks(np.arange(1, len(models)))
ax.set_xticklabels(names[1:])
ax.grid(True)
plt.show()
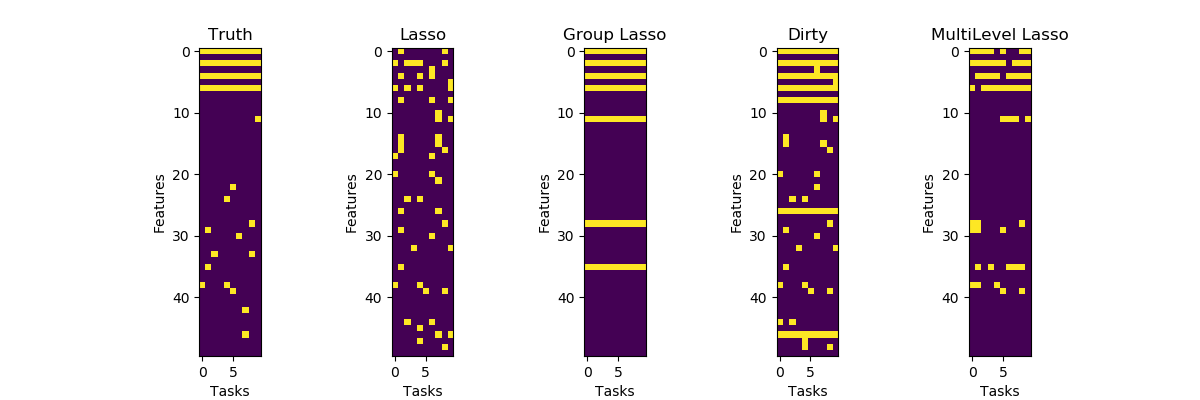
Plot the supports of the true and obtained coefficients for all models
f, axes = plt.subplots(1, 5, figsize=(12, 4))
for i, (ax, model, name) in enumerate(zip(axes, models, names)):
if i == 0:
ax.imshow(coef != 0)
else:
ax.imshow(model.coef_ != 0)
ax.set_title(name)
ax.set_xlabel("Tasks")
ax.set_ylabel("Features")
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 1.032 seconds)
Estimated memory usage: 13 MB